Test for Rates - Binomial Single Series Test
Intended audience: END-USERS DATA SCIENCE DEVELOPERS
AO Easy Answers: 4.3
Overview

The binomial analysis compares the values (count) of two categories to identify items that are significantly different from each other.
Purpose
The Binomial Test helps determine if one category's success rate is significantly different from another. It’s useful for comparing two outcomes to see if one truly performs better.
Business Example
Imagine a company that grows Apples, Oranges, and Bananas. They want to know if the yield of one fruit is significantly higher than the others.
Scenario
The company has past data on how much of each fruit was produced. They want to compare this data to see if one fruit's yield is noticeably different. For instance, if 60% of the yield is Apples and 40% is Oranges, they want to know if this difference is significant or just random.
To do this, they’ll use the Binomial Test, treating Apple yield as the “success” and comparing it to Oranges and Bananas.
Results
If the Binomial Test shows a significant result, it means Apple yields are truly higher, which may lead the company to focus more resources on Apples. If not, the yield difference might just be due to chance.
Data Sample
Fruit | Yield_Success | Yield_Volume |
|---|---|---|
Apple | 1 | 914 |
Banana | 0 | 111 |
Orange | 0 | 417 |
Apple | 1 | 691 |
Apple | 1 | 315 |
Apple | 1 | 438 |
Apple | 1 | 875 |
Banana | 0 | 760 |
Orange | 0 | 180 |
Infographics Insight
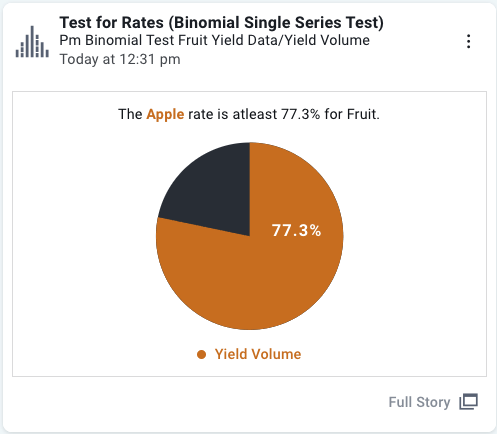
Full Story Insight
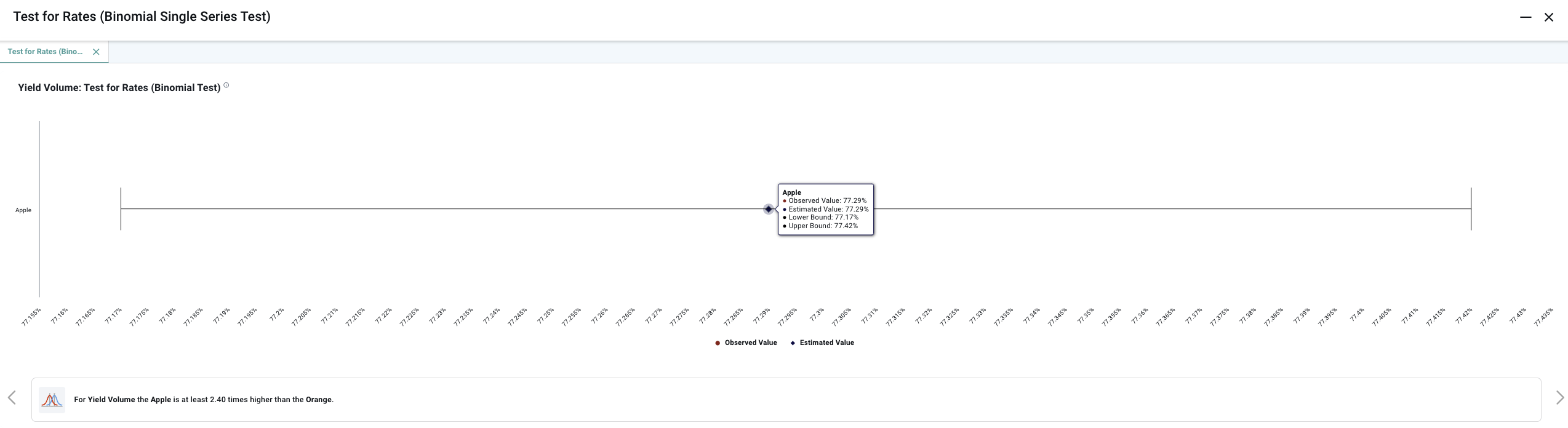
End User Configuration - using Easy Answers solution