Understanding Ontology
Intended audience: USERS
AO Easy Answers: 4.2
Overview
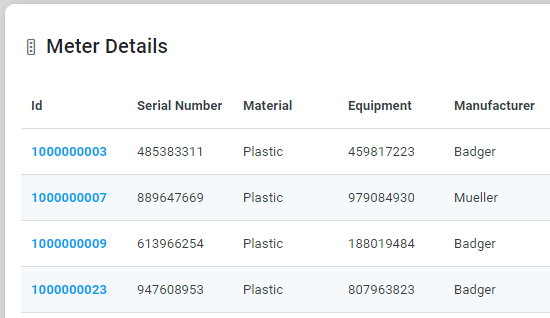
Underpinning each Easy Answers solution is an Ontology. An Ontology is the composition and interactions of all the “business objects” created for the solution. Say the Ontology is a “Utility Ontology”. Such Ontology will typically include business objects (MSOs) representing customers, assets, bills, contracts, projects, and issues of a Utility company. First view the Ontology by selecting the View Ontology option in the Options menu for the Natural Language Query field. A graphical representation of the Ontology will show as “nodes” (blue circles) and their relationship (blue rectangles), and for each node, “data fields” or properties are shown (green) with associated data types (orange).
Ontology example for a Water Utilities organization
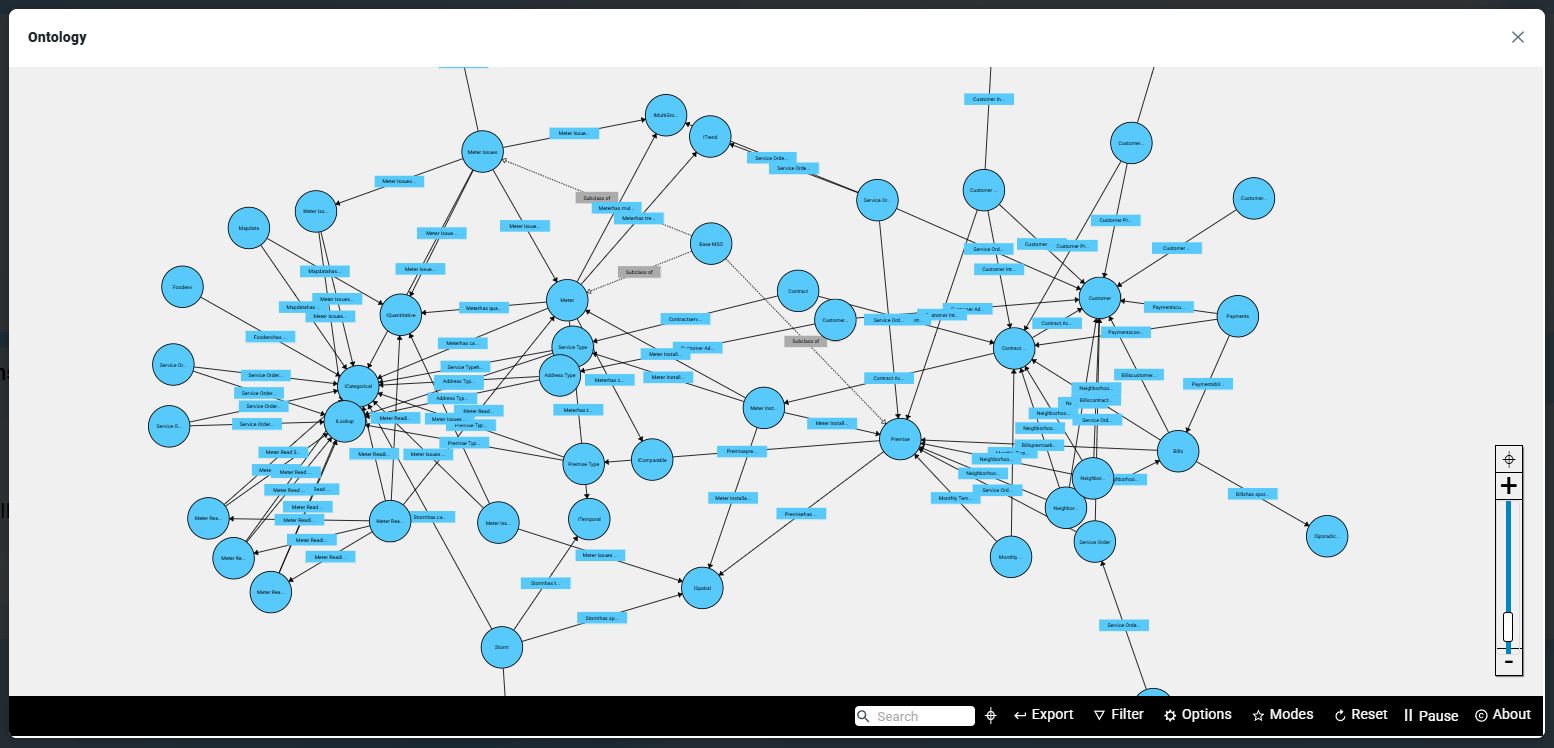
A single node in the Ontology for Meter assets and its data fields with data types
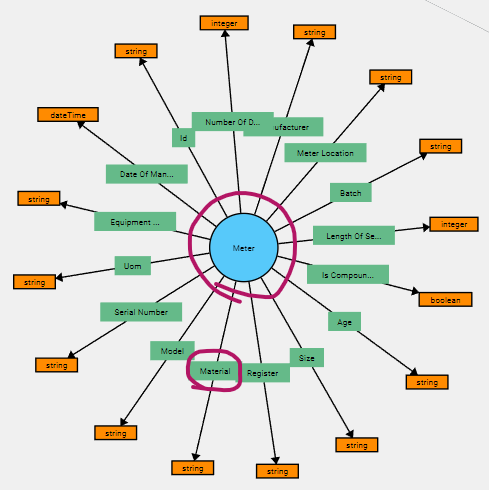
Say a node is labeled “Meter” as in a water-, gas- or electricity meter, and a data field for this node is labeled “Material”, this will inform the user that the following Natural Language Queries can be issued:
“Show all meters”.
“Show all plastic meters”.
The first query (“Show all meters”) may produce dashboard results that show all the data fields from the Meter node in which the user can find the data values for the Material field.
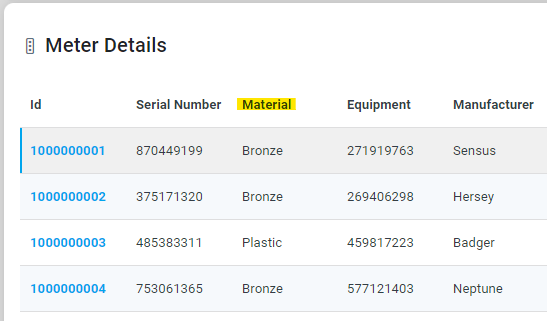
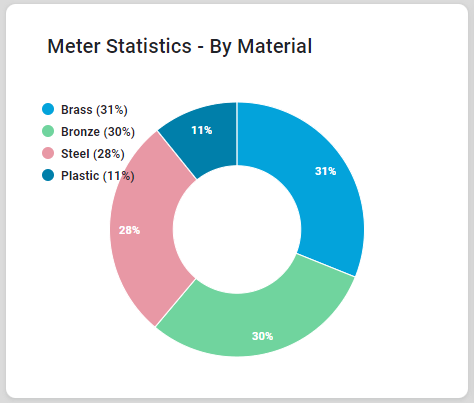
The second query - “Show all plastic meters” - relies on the system's understanding that “plastic” is a type of Material. For this to work, the creator of the Ontology needs to make the data values for the Material field in the Meter node into “Value Based Synonyms”. See MSO - Linguistics. With that insight, the user can now issue the second query.